How to Supercharge Your Super: The SMSF Strategy Australian Investors Swear By
In 2024, the Australian Taxation Office reported that Self-Managed Super Funds (SMSFs) now control nearly one-third of the nation’s $3.5 trillion superannuation pool, a staggering concentration of wealth in the hands of individual investors. Yet, behind this statistic lies a quieter revolution: a growing cohort of Australians rejecting the one-size-fits-all approach of traditional super funds in favor of the autonomy and tailored strategies SMSFs offer. For Raj and Linda Patel, both in their mid-40s, this shift meant leveraging their SMSF to acquire a commercial property in Melbourne—a move that not only diversified their portfolio but also provided a steady rental income stream aligned with their long-term retirement goals. Their story underscores a broader trend: SMSFs are not just about control; they are about crafting investment strategies that reflect personal ambitions, risk tolerances, and financial realities. But with this freedom comes complexity, demanding a level of diligence and expertise that few anticipate.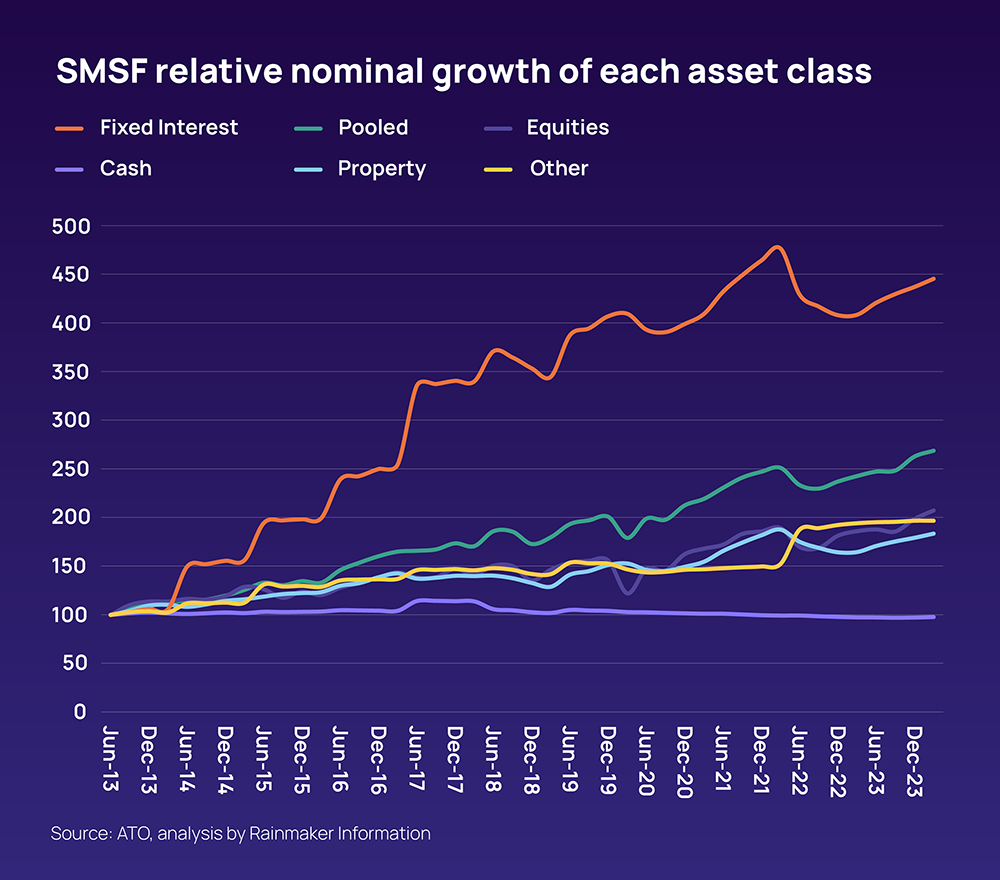
Image source: rainmaker.com.au
What Are SMSFs and How Do They Work?
A critical yet underexplored aspect of SMSFs is their ability to facilitate direct investment in alternative asset classes, such as commercial properties or private equity. Unlike traditional super funds, SMSFs empower trustees to tailor portfolios with assets that align closely with their financial goals and risk appetite. For instance, acquiring a commercial property through an SMSF not only diversifies holdings but also generates rental income, which can be reinvested or used to offset fund expenses. This approach, as demonstrated by Raj and Linda Patel’s Melbourne property acquisition, highlights the strategic advantage of leveraging SMSFs for tangible, income-producing assets.
However, this flexibility comes with stringent compliance requirements. Trustees must ensure that investments adhere to the sole purpose test—benefiting members’ retirement savings—and avoid breaches like personal use of fund assets. Additionally, the administrative burden, including maintaining detailed records and meeting tax obligations, demands a high level of diligence.
Emerging technologies, such as SMSF-specific accounting software, are mitigating these challenges by streamlining compliance and reporting. As SMSFs continue to evolve, integrating such tools with professional advisory services could redefine how Australians approach retirement planning, offering a balance between autonomy and expert oversight. This synergy may well shape the future of personalized wealth management.
Key Players: Trustees and Members
The dynamic between trustees and members in an SMSF is pivotal, as their dual roles demand both strategic foresight and operational precision. Trustees, who are often also members, must navigate a complex regulatory landscape while ensuring the fund’s investments align with the sole purpose test. A lesser-known but critical factor is the importance of trustee education. The Australian Taxation Office (ATO) emphasizes that trustees must possess sufficient financial literacy to make informed decisions, yet many overlook the value of ongoing training in areas like tax law updates and investment strategy optimization.
For example, trustees who proactively engage with SMSF-specific workshops or advisory services often outperform their peers in compliance and fund performance. This is particularly evident in scenarios involving complex asset classes, such as private equity or leveraged property investments, where nuanced understanding can mitigate risks.
Additionally, the choice between individual and corporate trustee structures significantly influences fund governance. Corporate trustees, while costlier to establish, offer enhanced asset protection and continuity, especially in cases of member turnover.
Looking ahead, integrating trustee education with emerging technologies, such as AI-driven compliance tools, could redefine SMSF management, fostering a more resilient and adaptive approach to retirement planning.
Regulatory Framework and Compliance
The regulatory framework governing SMSFs is both a safeguard and a challenge, designed to ensure funds operate solely for members’ retirement benefits. Trustees must comply with the Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Act 1993 (SISA) and related regulations, which impose strict rules on investment choices, reporting, and fund management. For instance, investments must adhere to the arm’s length principle, prohibiting transactions with related parties unless explicitly allowed. Breaching this rule can result in severe penalties, including loss of compliance status.
A common misconception is that professional assistance absolves trustees of responsibility. However, the Australian Taxation Office (ATO) holds trustees personally accountable, even when external advisors are involved. This underscores the importance of trustee education, as demonstrated by workshops that improve compliance rates and fund performance.
Emerging technologies, such as SMSF-specific accounting software, are transforming compliance. These tools streamline tasks like annual return preparation and real-time monitoring of contribution caps. By integrating such innovations with professional advice, trustees can navigate complexities more effectively, ensuring both compliance and strategic fund growth.
Image source: coastaladvicegroup.com.au
Navigating ATO Guidelines and the SIS Act
A critical yet often overlooked aspect of navigating ATO guidelines and the Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Act 1993 (SIS Act) is the requirement for SMSF trustees to maintain a written, tailored investment strategy. This document must address key factors such as risk, diversification, liquidity, and the fund’s ability to meet liabilities. Failure to comply can result in penalties of up to $4,440 per trustee, underscoring the high stakes of non-compliance.
One effective approach is leveraging scenario-based planning. For example, trustees can model potential market downturns to assess whether their fund’s liquidity is sufficient to cover member benefits and operational costs. This proactive strategy aligns with the SIS Act’s emphasis on prudential risk management while ensuring compliance with ATO expectations.
Another underutilized tool is SMSF-specific accounting software, which integrates real-time monitoring of contribution caps and asset allocations. These platforms not only streamline compliance but also provide actionable insights, such as identifying underperforming assets that may jeopardize diversification requirements.
Trustees should also consider periodic reviews of their strategy, particularly after major life events or market shifts. By embedding adaptability into their compliance framework, SMSFs can balance regulatory obligations with long-term growth objectives, setting a precedent for resilient and forward-thinking fund management.
Understanding Compliance Obligations
A nuanced yet pivotal compliance obligation for SMSF trustees is adhering to the sole purpose test, which mandates that all fund activities must exclusively benefit members’ retirement savings. While straightforward in theory, practical application often reveals complexities, particularly when investments intersect with personal interests. For instance, leasing a commercial property owned by the SMSF to a related business may breach compliance unless it satisfies the arm’s length principle.
To navigate this, trustees can implement independent valuation protocols. Engaging third-party valuers ensures that transactions reflect market rates, mitigating risks of non-compliance. This approach not only satisfies ATO scrutiny but also reinforces the fund’s integrity.
Another overlooked aspect is the requirement to document compliance actions meticulously. Trustees should maintain detailed records of investment decisions, including minutes of meetings and supporting evidence for asset valuations. These records serve as critical safeguards during audits, reducing the likelihood of penalties.
Emerging technologies, such as AI-driven compliance tools, are transforming how trustees meet these obligations. These platforms automate record-keeping and flag potential breaches in real time, enabling proactive management. By integrating such tools with professional advice, trustees can foster a culture of compliance while positioning their SMSFs for sustainable growth in an increasingly regulated environment.
Developing a Robust Investment Strategy
Crafting a robust SMSF investment strategy requires balancing compliance with personalized financial goals. A common misconception is that diversification alone ensures success. However, true robustness lies in aligning asset allocation with members’ unique circumstances, such as age, risk tolerance, and retirement timelines. For instance, younger members may prioritize growth assets like equities, while older members might focus on income-generating investments such as bonds or commercial property.
Unexpectedly, liquidity often becomes a blind spot. Trustees may overlook the need for readily accessible funds to cover unexpected expenses or member benefits. A practical example is maintaining a portion of the fund in cash or liquid assets to meet tax obligations or pension payments without disrupting long-term investments.
Expert insights emphasize the importance of scenario testing. By modeling potential market downturns, trustees can evaluate whether their strategy withstands volatility. For example, stress-testing a portfolio against a 20% equity market drop can reveal vulnerabilities in over-concentrated holdings.
Integrating technology, such as SMSF-specific accounting software, further enhances strategy resilience. These tools provide real-time insights into asset performance and compliance risks, enabling trustees to adapt dynamically. Ultimately, a robust strategy is not static but evolves with changing member needs and market conditions.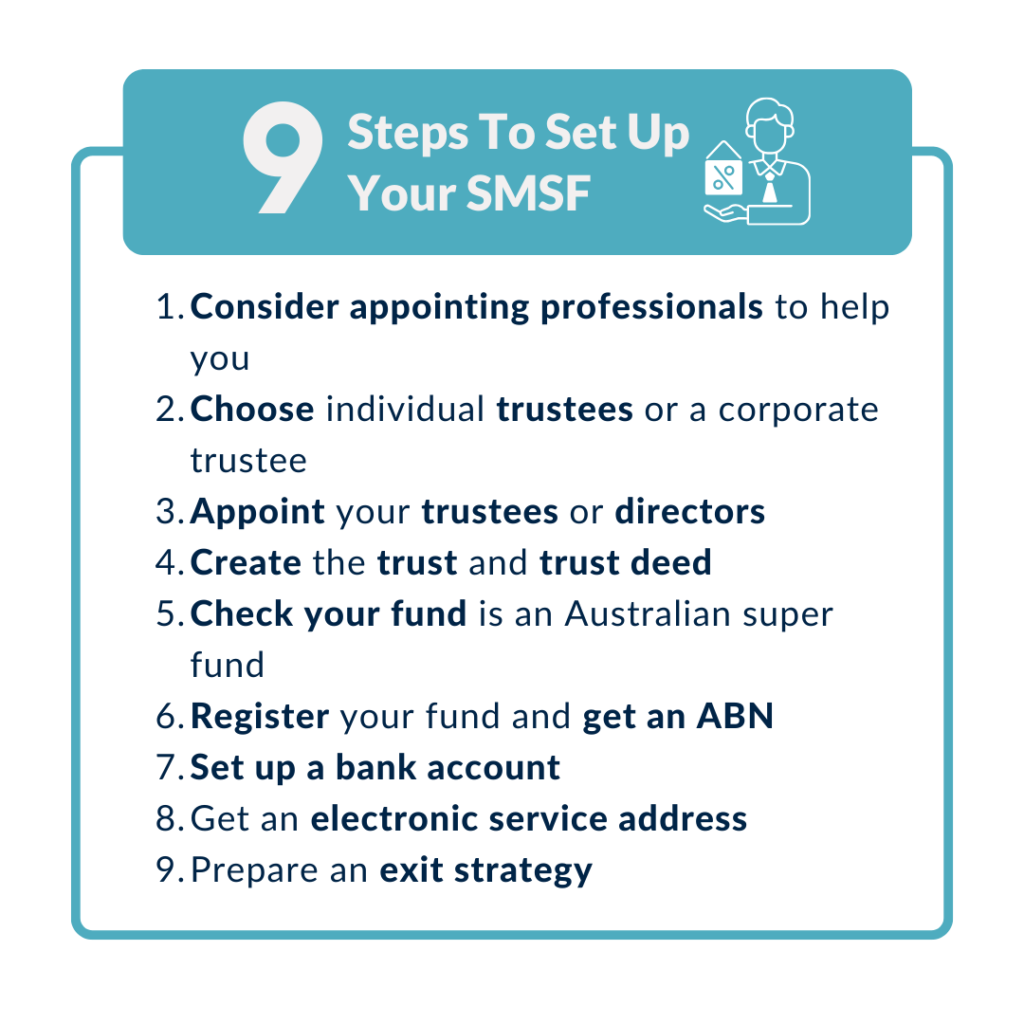
Image source: coastaladvicegroup.com.au
Risk Assessment and Asset Allocation
Effective risk assessment in SMSF asset allocation extends beyond traditional diversification. While spreading investments across asset classes is foundational, trustees often overlook correlation risk—the tendency of assets to move in tandem during market downturns. For example, equities and property markets may both decline during economic recessions, leaving portfolios exposed despite appearing diversified. Incorporating uncorrelated assets, such as government bonds or alternative investments like infrastructure funds, can mitigate this risk.
Another critical yet underappreciated factor is sequence-of-returns risk. This risk disproportionately affects members nearing retirement, as early losses in a drawdown phase can erode capital faster than later losses. Trustees can address this by allocating a portion of the portfolio to low-volatility assets, such as cash or fixed income, ensuring liquidity for pension payments during volatile periods.
Real-world applications highlight the importance of dynamic asset allocation. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, SMSFs that rebalanced portfolios to capitalize on undervalued equities outperformed static strategies. This underscores the value of periodic reviews and adjustments.
Emerging tools, such as AI-driven portfolio analytics, offer actionable insights by identifying underperforming assets and stress-testing allocations against hypothetical scenarios. By integrating these technologies, trustees can proactively manage risks, ensuring alignment with both compliance and long-term growth objectives.
Diversification and Liquidity Considerations
A nuanced aspect of diversification and liquidity in SMSFs is the interplay between asset concentration and cash flow management. While diversification reduces risk, over-diversification can dilute returns and increase administrative complexity. Trustees must strike a balance by aligning asset allocation with the fund’s liquidity needs and members’ retirement timelines.
For example, SMSFs heavily invested in illiquid assets like property may face challenges in meeting unexpected liabilities, such as death benefits or pension payments. A practical approach is maintaining a liquidity buffer—allocating a portion of the portfolio to highly liquid assets like cash or short-term fixed interest. This ensures the fund can meet obligations without prematurely liquidating long-term investments at unfavorable prices.
Emerging strategies, such as liquidity stress testing, allow trustees to simulate scenarios like market downturns or sudden member withdrawals. By analyzing these outcomes, trustees can adjust their asset mix to ensure resilience. For instance, during the 2020 market volatility, funds with diversified liquidity sources—combining equities, bonds, and cash—were better positioned to weather disruptions.
Integrating real-time analytics tools can further enhance decision-making. These platforms provide insights into liquidity ratios and asset performance, enabling trustees to dynamically adapt strategies, ensuring both compliance and financial stability in evolving market conditions.
Advanced SMSF Strategies
Advanced SMSF strategies often leverage gearing and alternative investments to amplify returns, but these approaches demand precision and foresight. For instance, borrowing within an SMSF to acquire property can magnify gains during market upswings. However, trustees must navigate strict compliance rules, such as ensuring the loan adheres to a limited recourse borrowing arrangement (LRBA), which protects other fund assets from creditor claims.
A compelling example is the rise of private equity investments within SMSFs. Unlike traditional equities, private equity offers access to high-growth opportunities but requires trustees to assess liquidity constraints and extended investment horizons. For example, funds that allocated to private equity during the 2010s often outperformed public markets, showcasing the potential for long-term gains.
Emerging technologies, such as AI-driven analytics, now enable trustees to model these strategies under various scenarios, identifying risks like sequence-of-returns volatility. By integrating these tools, SMSFs can balance ambition with prudence, ensuring compliance while pursuing innovative growth pathways.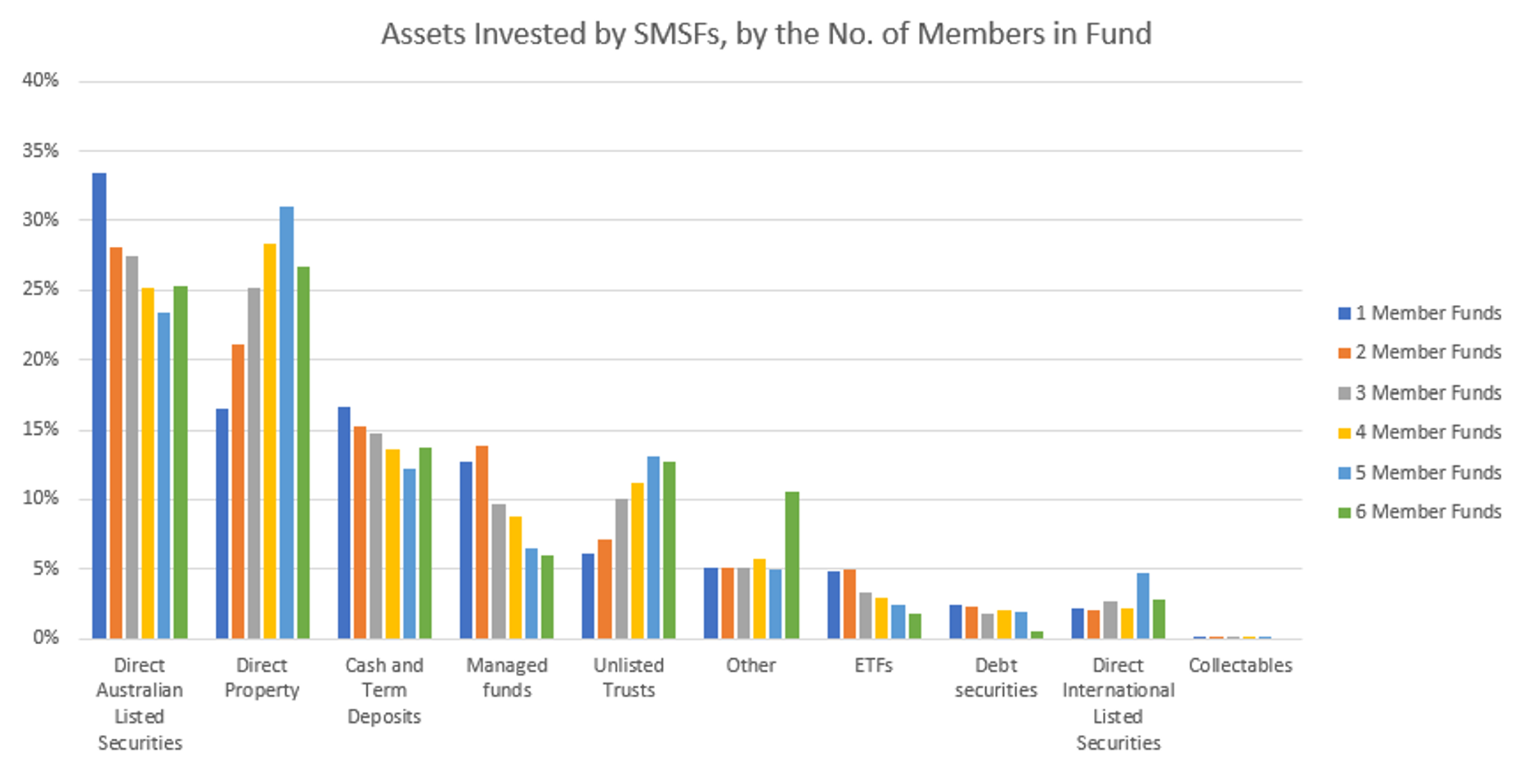
Image source: findex.com.au
Property Investment and LRBAs
A critical yet underexplored dimension of property investment through Limited Recourse Borrowing Arrangements (LRBAs) is the interplay between loan structure and asset performance. Unlike traditional loans, LRBAs limit the lender’s recourse to the purchased asset, safeguarding other SMSF assets. However, this protection comes at a cost: higher interest rates—typically 2–3% above standard loans—and stricter loan-to-value ratio (LVR) requirements, often capped at 60–70%.
For example, an SMSF acquiring a commercial property in Sydney through an LRBA must account for not only the deposit but also ancillary costs like stamp duty, legal fees, and insurance. These expenses, paid directly from the SMSF, can strain liquidity if not planned meticulously. Trustees must also ensure the property aligns with the fund’s investment strategy, balancing risk, return, and diversification.
A lesser-known but pivotal factor is the arm’s length principle. Transactions involving related parties, such as leasing the property to a member’s business, must reflect market rates to avoid compliance breaches. Independent valuations and detailed documentation are essential to satisfy ATO scrutiny.
Emerging technologies, such as AI-driven property analytics, are transforming how trustees evaluate potential investments. These tools provide real-time insights into market trends, rental yields, and risk factors, enabling data-driven decisions. By integrating such technologies with professional advice, SMSFs can optimize property investments while maintaining compliance, setting a precedent for strategic growth in an increasingly regulated environment.
Incorporating Estate Planning
A pivotal yet underutilized aspect of SMSF estate planning is the strategic use of binding death benefit nominations (BDBNs) to ensure precise asset distribution. Unlike standard wills, BDBNs allow trustees to bypass probate, reducing delays and potential disputes. However, their effectiveness hinges on strict adherence to the SMSF trust deed and regular updates to reflect changing circumstances, such as new dependents or marital status.
For instance, a trustee who fails to update a BDBN after divorce risks unintentionally directing benefits to an ex-spouse. To mitigate such risks, trustees should integrate conditional BDBNs, which specify alternate beneficiaries if primary nominees are no longer eligible. This approach not only enhances flexibility but also aligns with evolving family dynamics.
Another overlooked factor is the tax impact on non-dependent beneficiaries. Death benefits paid to adult children, for example, may attract significant tax liabilities. Establishing a testamentary trust within the estate plan can mitigate this by enabling tax-effective income distribution across multiple beneficiaries.
Emerging technologies, such as estate planning software, now streamline the integration of BDBNs with broader SMSF strategies. By leveraging these tools alongside professional advice, trustees can create dynamic, tax-efficient plans that adapt to both regulatory changes and personal milestones, ensuring long-term financial security for beneficiaries.
Ongoing Management and Best Practices
Effective SMSF management demands a proactive approach, blending regular oversight with strategic adaptability. A common misconception is that annual reviews suffice; however, quarterly monitoring of contributions, expenses, and asset performance ensures alignment with both compliance and investment goals. For example, during the 2020 market volatility, SMSFs that rebalanced portfolios quarterly outperformed those with static strategies, highlighting the value of frequent adjustments.
Trustees should also embrace scenario-based planning to anticipate potential disruptions. Modeling events like sudden member withdrawals or market downturns can reveal liquidity gaps, enabling preemptive action. Emerging tools, such as AI-driven analytics, further enhance this process by providing real-time insights into fund performance and compliance risks.
Additionally, integrating professional advice with technology fosters a balanced approach. This synergy not only mitigates errors but also positions SMSFs for sustainable growth in dynamic market conditions.
Image source: morrows.com.au
Record-Keeping and Auditing Requirements
A critical yet often underestimated aspect of SMSF management is the precision required in record-keeping to ensure compliance and facilitate seamless audits. Trustees must maintain detailed documentation of all transactions, investment decisions, and asset valuations, as mandated by the Australian Taxation Office (ATO). For instance, failure to retain records for at least five years can result in penalties or loss of compliance status.
One effective approach is leveraging digital record-keeping systems that integrate with SMSF-specific accounting software. These platforms automate data entry, flag missing documentation, and provide real-time audit trails, reducing human error. For example, AI-driven tools can cross-reference bank statements with investment records, ensuring consistency and accuracy.
A lesser-known but pivotal factor is the requirement to document compliance with the arm’s length principle. For property investments, trustees should retain independent valuations and lease agreements to demonstrate market-rate transactions. This not only satisfies regulatory scrutiny but also reinforces fund integrity.
Looking ahead, integrating blockchain technology for immutable record-keeping could revolutionize SMSF audits by providing verifiable, tamper-proof transaction histories. By adopting such innovations, trustees can enhance transparency, streamline compliance, and position their funds for long-term resilience in an increasingly regulated environment.
Regular Strategy Reviews and Professional Advice
A focused yet underutilized aspect of regular strategy reviews is the integration of stress-testing scenarios to evaluate the resilience of an SMSF investment strategy. By simulating adverse market conditions, such as a 20% equity market drop or a sudden liquidity crisis, trustees can identify vulnerabilities in their portfolio and adjust allocations proactively. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, SMSFs that incorporated stress-testing were better positioned to rebalance portfolios and capitalize on undervalued assets.
Professional advice plays a pivotal role in enhancing these reviews. Financial advisors equipped with SMSF-specific expertise can provide insights into market trends, regulatory updates, and tax-efficient strategies. For example, James McFall, Managing Director of Yield Financial Planning, emphasizes the importance of aligning reviews with significant life events, such as a member transitioning to pension phase, to ensure the strategy remains relevant.
A lesser-known but impactful approach is leveraging AI-driven analytics tools during reviews. These platforms offer real-time insights into asset performance, compliance risks, and diversification gaps, enabling data-driven decisions. By combining these technologies with professional guidance, trustees can foster a dynamic, forward-looking strategy that adapts to both market shifts and evolving member needs, ensuring long-term fund sustainability.
FAQ
What are the key benefits of using an SMSF for retirement planning in Australia?
Self-Managed Super Funds (SMSFs) offer unparalleled control over investment decisions, allowing trustees to tailor portfolios to their financial goals and risk tolerance. Key benefits include access to diverse asset classes, such as property and private equity, enabling strategic diversification and risk mitigation. SMSFs also provide significant tax advantages, including concessional tax rates on income and capital gains, enhancing wealth accumulation. Additionally, they facilitate estate planning and intergenerational wealth transfer, ensuring assets are distributed tax-effectively. By integrating advanced tools like AI-driven analytics, SMSFs empower trustees to optimize compliance and performance, making them a powerful vehicle for retirement planning in Australia.
How does the SMSF investment strategy align with compliance requirements under the SIS Act?
An SMSF investment strategy must comply with the Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Act 1993 (SIS Act) by addressing key factors such as risk, diversification, liquidity, and the fund’s ability to meet liabilities. Trustees are required to document a written strategy tailored to members’ circumstances, ensuring alignment with the sole purpose test. Regular reviews and updates are essential to maintain compliance, particularly after significant life events or market shifts. Leveraging tools like SMSF-specific accounting software enhances adherence by automating record-keeping and monitoring. This alignment safeguards the fund’s compliance status while optimizing its performance and long-term sustainability.
What role do diversification and liquidity play in optimizing SMSF performance?
Diversification mitigates risk by spreading investments across asset classes, sectors, and geographies, reducing exposure to underperforming assets while enhancing long-term returns. Liquidity ensures the SMSF can meet obligations like pension payments, taxes, and unexpected expenses without disrupting long-term investments. A balanced portfolio combining liquid assets, such as cash or bonds, with illiquid ones, like property, optimizes both stability and growth potential. Regular liquidity stress testing and diversification reviews, supported by AI-driven analytics, enable trustees to adapt dynamically to market conditions. Together, these elements ensure compliance, financial resilience, and alignment with retirement goals, maximizing SMSF performance.
How can emerging technologies like AI-driven tools enhance SMSF management and compliance?
AI-driven tools revolutionize SMSF management by automating compliance tasks, such as real-time monitoring of contribution caps and asset allocations, ensuring adherence to the SIS Act. These technologies enhance decision-making through predictive analytics, identifying underperforming assets and optimizing diversification strategies. By streamlining record-keeping and generating audit-ready reports, AI reduces administrative burdens and mitigates human error. Integration with SMSF-specific accounting software provides actionable insights into fund performance and compliance risks. This synergy empowers trustees to navigate complex regulations efficiently, adapt to market dynamics, and focus on strategic growth, ultimately enhancing the fund’s long-term sustainability and financial outcomes.
What are the critical steps to developing a robust SMSF investment strategy tailored to individual goals?
Developing a robust SMSF investment strategy begins with assessing members’ financial goals, risk tolerance, and retirement timelines to establish a personalized foundation. Define clear, measurable objectives aligned with these goals, ensuring compliance with the sole purpose test. Strategically allocate assets across diverse classes, balancing growth and stability while maintaining liquidity for obligations. Incorporate scenario testing to evaluate resilience against market volatility and adjust allocations proactively. Regularly review and update the strategy to reflect life changes or economic shifts. Leveraging AI-driven analytics and professional advice enhances precision, ensuring the strategy remains compliant, adaptive, and aligned with long-term financial aspirations.