The Superannuation Myth That’s Holding Australians Back From Building Wealth
Australia’s superannuation system, often hailed as a cornerstone of financial security, is shrouded in misconceptions that quietly erode its potential. One of the most pervasive myths is that superannuation is a passive, set-and-forget mechanism, leaving many Australians disengaged from actively shaping their financial futures. In today’s climate of rising living costs and economic uncertainty, this mindset could be the very barrier preventing individuals from building substantial wealth. What if the key to unlocking your super’s full potential lies in challenging this assumption? By rethinking how we approach superannuation, we can uncover opportunities to transform retirement savings into a dynamic wealth-building tool.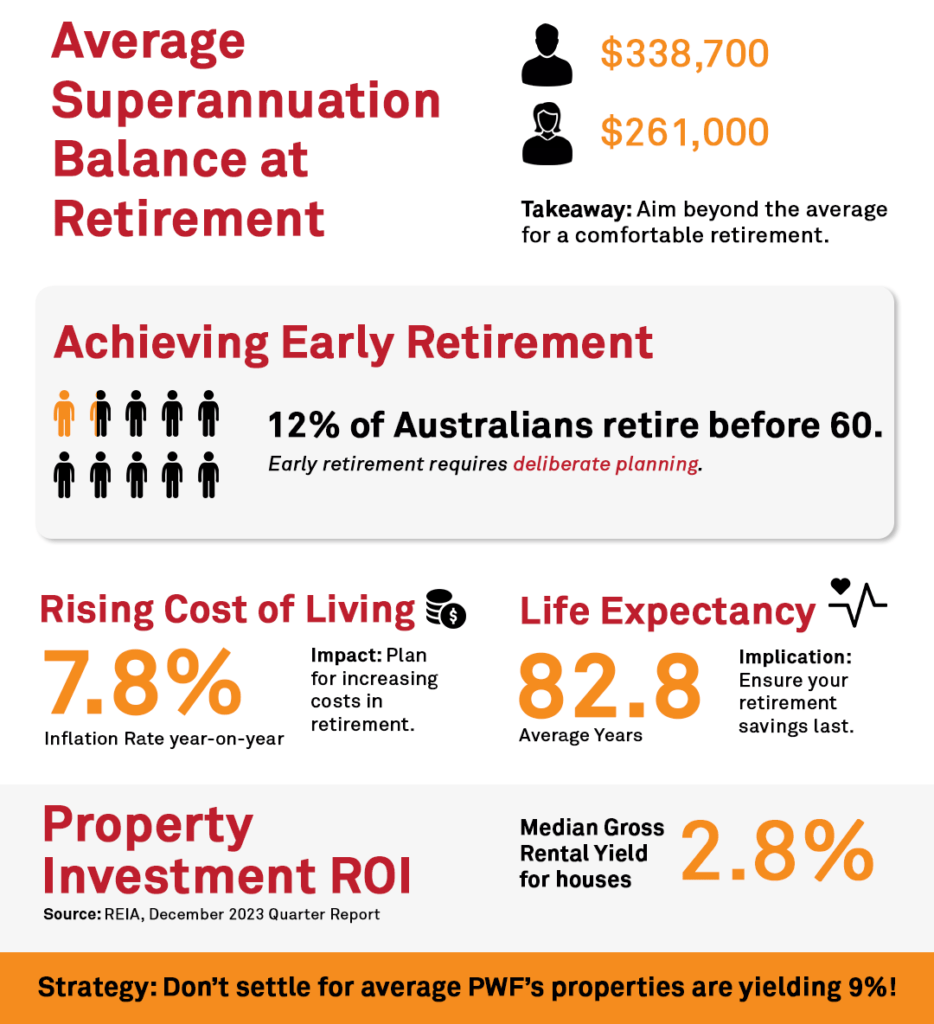
Image source: simplywealthgroup.com.au
Why Superannuation Matters
Superannuation is more than a retirement fund—it’s a tax-effective investment vehicle with the potential to outpace traditional savings methods. By leveraging compound interest and strategic asset allocation, individuals can significantly amplify their wealth over time. For instance, younger Australians who actively manage their super can benefit from higher-risk, growth-oriented investments, capitalising on decades of market cycles. Moreover, legislative changes, such as the removal of the $450 monthly earnings threshold, now enable even low-income earners to build their super early. This underscores the importance of financial literacy and proactive engagement, transforming superannuation into a dynamic tool for long-term financial empowerment.
Defining the Myth and Its Origins
The myth that superannuation is a passive, “set-and-forget” system stems from its design as a compulsory savings mechanism. While this structure ensures participation, it inadvertently fosters disengagement, as many Australians assume professional fund managers alone dictate outcomes. This misconception is compounded by limited financial literacy and the complexity of investment options, which deter active involvement. However, evidence shows that individuals who consolidate accounts, review fund performance, and align investments with personal goals often achieve superior outcomes. By reframing superannuation as a participatory tool, Australians can shift from passive reliance to proactive wealth-building, unlocking its full potential for future security.
Unpacking the Superannuation Myth
The belief that superannuation operates independently of personal input is akin to assuming a garden will thrive without tending. Research from the Superannuation and Retirement Insights Report reveals that individuals who actively manage their super—by consolidating accounts, adjusting contributions, or selecting tailored investment options—achieve significantly higher returns. For example, a 30-year-old increasing contributions by just 1% could see an additional $100,000 by retirement, thanks to compound growth. This myth persists due to financial jargon and perceived complexity, but with accessible tools and expert advice, Australians can transform their super from a passive fund into a thriving financial ecosystem.

Image source: ivypanda.com
Common Misconceptions About Retirement Savings
A prevalent misconception is that low fees guarantee better superannuation outcomes. While fees matter, net returns—the performance after fees—are the true measure of success. For instance, a fund with slightly higher fees but superior long-term growth can outperform a low-fee fund with stagnant returns. Additionally, many overlook the impact of voluntary contributions, assuming employer contributions suffice. Yet, even modest additional contributions early in life can exponentially grow through compounding. By shifting focus from cost minimization to strategic growth and leveraging tools like salary sacrifice, Australians can align their super strategies with broader financial goals, ensuring a more robust retirement.
Realities Behind Australia’s Retirement Income System
Australia’s three-pillar retirement income system—comprising the Age Pension, compulsory superannuation, and private savings—offers flexibility but also reveals disparities. For instance, home ownership, often overlooked, significantly impacts retirement outcomes. Retirees who own homes outright face lower living costs, enabling superannuation to stretch further, while renters risk financial strain. Additionally, the system’s reliance on market performance means economic downturns can disproportionately affect those nearing retirement. Addressing these realities requires integrating financial literacy programs and policies that support housing stability. By aligning superannuation strategies with broader economic factors, Australians can mitigate risks and enhance the system’s capacity to deliver equitable outcomes.
Understanding the Tax Concessions
Superannuation tax concessions, while designed to incentivize retirement savings, disproportionately benefit high-income earners. For example, contributions taxed at 15% provide greater relief to those in higher tax brackets compared to low-income earners. This creates a regressive effect, where wealthier individuals amplify their savings advantage. Additionally, the tax-free status of earnings in the pension phase for those over 60 further skews benefits. A lesser-known factor is the opportunity cost for low-income earners, who might prioritize immediate needs over voluntary contributions. Addressing these imbalances through targeted reforms could enhance equity, ensuring concessions better support those most reliant on superannuation in retirement.
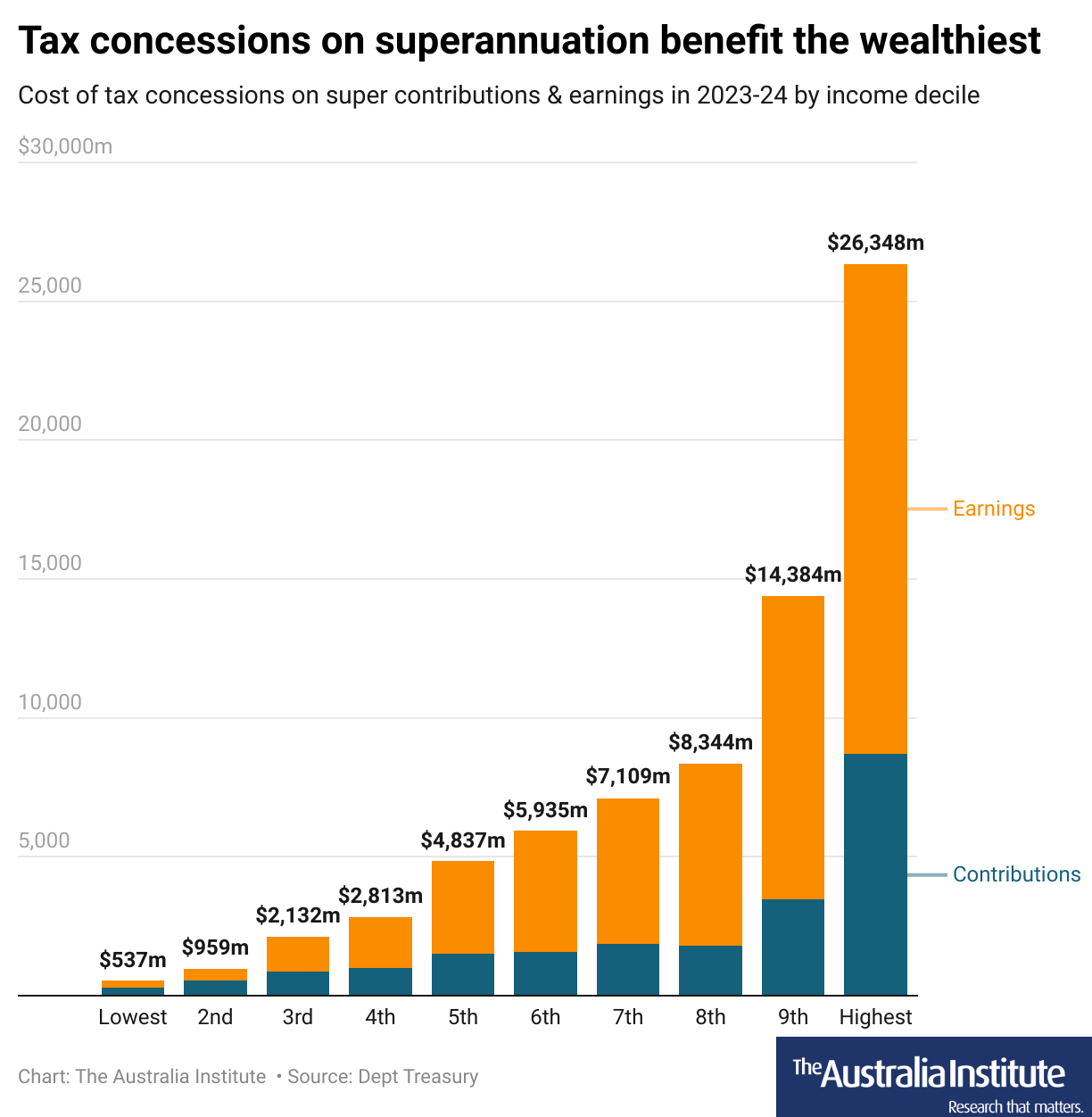
Image source: australiainstitute.org.au
How Tax Benefits Assist Wealth Accumulation
Tax concessions on superannuation contributions act as a multiplier effect for wealth accumulation, particularly through concessional contributions. For instance, salary sacrificing into super reduces taxable income while enabling pre-tax dollars to grow within a low-tax environment. This dual advantage accelerates compounding returns over decades. However, lesser-known strategies, such as spouse contributions or the downsizer contribution, can further optimize tax efficiency, especially for couples. These approaches not only reduce immediate tax liabilities but also align with estate planning goals. By integrating these strategies with broader financial plans, individuals can maximize long-term wealth while navigating evolving legislative frameworks with confidence.
Disparities in Who Truly Benefits
Superannuation tax concessions amplify existing income inequalities, with 54% of concessional benefits flowing to the top 20% of earners. This imbalance stems from higher-income individuals’ ability to maximize voluntary contributions and leverage tax advantages unavailable to lower earners. For example, low-income earners often forgo contributions due to immediate financial pressures, missing out on compounding benefits. Additionally, women, who are more likely to work part-time, face systemic disadvantages in accessing these concessions. Addressing these disparities requires targeted reforms, such as scaling concessions based on income or introducing mechanisms like co-contributions to ensure equitable access to retirement savings growth.
Economic and Social Implications
Superannuation’s design as a wealth-building tool extends beyond individual benefits, driving broader economic stability. For instance, its role in offsetting the fiscal strain of an ageing population reduces reliance on public pensions, as highlighted in economic models. However, misconceptions persist—such as the belief that superannuation solely benefits high-income earners. While disparities exist, targeted reforms could amplify its social impact, fostering equity. Analogous to a well-tended ecosystem, superannuation thrives when contributions, tax policies, and financial literacy align. By addressing systemic gaps, such as gender inequities, superannuation can evolve into a cornerstone of both personal security and national economic resilience.
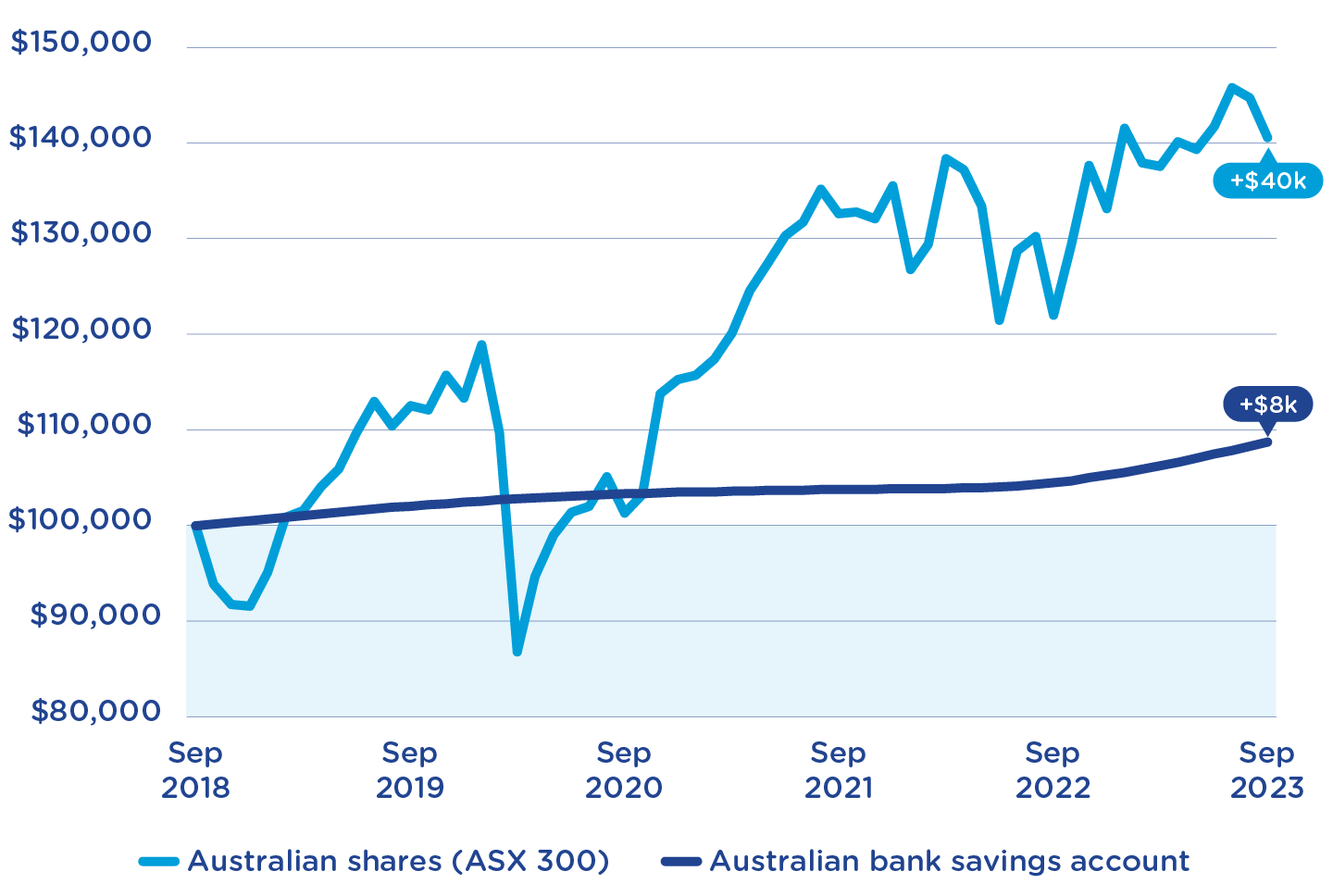
Image source: rest.com.au
Effects on Wealth Distribution and Inequality
Superannuation has reshaped wealth distribution by broadening asset ownership beyond the wealthiest 10%, as evidenced by increased exposure to equities and infrastructure among middle-income earners. However, its unequal distribution persists, with older Australians holding disproportionate balances due to compounding advantages. Lesser-known factors, such as the regressive impact of tax concessions, exacerbate this divide. Integrating policies like income-scaled contributions or incentivizing low-income participation could mitigate disparities. Additionally, aligning superannuation with housing affordability strategies could address the “asset rich, income poor” paradox, fostering a more equitable system that balances wealth accumulation with immediate financial security.
Impact on National Savings and Economic Growth
Superannuation’s contribution to national savings extends beyond individual accounts, creating a robust capital pool that underpins domestic investment. For example, the Treasury estimated that increasing the Superannuation Guarantee to 12% could boost national savings to over 2% of GDP, driving productivity and higher living standards. Lesser-known dynamics, such as its role in reducing reliance on volatile foreign capital, further stabilize economic growth. By channeling these funds into infrastructure and innovation, superannuation can act as a catalyst for long-term economic resilience. Policymakers should prioritize frameworks that align superannuation investments with national priorities, ensuring sustainable growth and equitable wealth distribution.
Rethinking Wealth-Building Strategies
Wealth-building through superannuation requires a shift from passive accumulation to active strategy. For instance, reallocating funds into growth-oriented assets during early career stages can yield exponential returns, as shown by a 2023 study linking diversified portfolios to 20% higher balances over 30 years. Misconceptions, like prioritizing low fees over net returns, often hinder growth. Instead, leveraging tools like salary sacrifice or spouse contributions can optimize tax efficiency and compounding. Analogous to fine-tuning an engine, aligning super investments with life goals ensures peak performance. By integrating financial literacy and expert advice, Australians can transform superannuation into a dynamic wealth-building framework.
Image source: leadingadvice.com.au
Aligning Long-Term Goals with Superannuation
Tailoring superannuation strategies to life stages unlocks its full potential. For example, younger individuals can prioritize growth assets, leveraging decades of compounding, while those nearing retirement may shift to defensive investments to preserve capital. A lesser-known approach involves aligning super contributions with major life events, such as using the downsizer contribution after selling a home to boost retirement savings. Additionally, integrating superannuation planning with estate strategies ensures intergenerational wealth transfer. By viewing super as a dynamic tool rather than a static fund, Australians can bridge immediate needs with future aspirations, fostering both financial security and generational impact.
Diversification and Alternative Investments
Diversification within superannuation extends beyond traditional asset classes like equities and bonds. Incorporating alternative investments—such as infrastructure, private equity, or Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)—can enhance risk-adjusted returns. For instance, REITs provide exposure to property markets without the capital intensity of direct ownership, offering liquidity and sector diversification. Lesser-known options, like unlisted infrastructure, deliver stable, long-term yields less correlated with market volatility. By balancing these alternatives with core holdings, individuals can mitigate risks tied to economic cycles. This approach, akin to constructing a resilient ecosystem, ensures super portfolios adapt to changing market conditions while maximizing growth opportunities.
FAQ
What is the most common misconception about superannuation, and how does it impact wealth-building?
The most common misconception is that superannuation is a passive, “set-and-forget” system. This belief discourages active engagement, leading to missed opportunities for optimizing returns through strategies like tailored investments or voluntary contributions. By challenging this myth, Australians can transform their super into a proactive wealth-building tool, unlocking its full potential.
How can Australians actively manage their superannuation to maximize long-term returns?
Australians can maximize long-term returns by consolidating accounts, regularly reviewing fund performance, and aligning investments with personal goals. Strategies like salary sacrifice, voluntary contributions, and diversifying portfolios into growth-oriented assets early on are key. Staying informed about legislative changes and seeking professional advice further enhances superannuation outcomes.
What role do tax concessions play in enhancing superannuation growth, and who benefits the most?
Tax concessions accelerate superannuation growth by reducing taxable income and enabling pre-tax contributions to grow in a low-tax environment. However, high-income earners benefit disproportionately, leveraging these concessions to amplify savings. Addressing this imbalance through targeted reforms could ensure equitable access, enhancing retirement outcomes for lower-income Australians.
How does diversification within superannuation portfolios contribute to financial resilience?
Diversification reduces risk by spreading investments across asset classes, industries, and regions, minimizing reliance on any single market. This approach stabilizes returns during market fluctuations and enhances growth potential. Incorporating alternatives like infrastructure or international equities further strengthens portfolios, ensuring financial resilience against economic uncertainties and sector-specific downturns.
What strategies can individuals use to align their superannuation with their life and retirement goals?
Individuals can align superannuation with life and retirement goals by tailoring contributions to life stages, prioritizing growth assets early, and shifting to defensive investments near retirement. Utilizing tools like the downsizer contribution, consolidating accounts, and integrating estate planning ensures superannuation supports both immediate needs and long-term aspirations effectively.